Knowing about lock parts is very important for keeping your home or business safe. When you learn about these parts, you can make your security better. Locks have different parts. Some are electronic, like sensors and circuits. Others use biometrics, like scanners and databases. Each part helps make your lock stronger. In this guide, we will learn about these parts. We will see what they do and how they keep your things safe. Let’s start learning about lock security together.
What Are The Component Of The Lock?
Basic Components of the lock
To understand a lock, we need to look at its main parts: the key, cylinder, and latch or bolt. Each part plays a big role in keeping things safe and controlling who can get in.
Key: The Gate Opener
Use: A key is more than a piece of metal. It’s the way to get into locked spaces. The key’s job is to line up with the lock’s inside parts. This lets it turn and open the lock. If you don’t have the right key, the lock won’t open.
Kinds: There are many kinds of keys for different locks and security needs. Regular metal keys have special patterns of grooves and ridges. People use these keys a lot with mechanical locks. Electronic keys, like keycards or fobs, use technology. They can set off electronic locks, which is handy and offers more security.
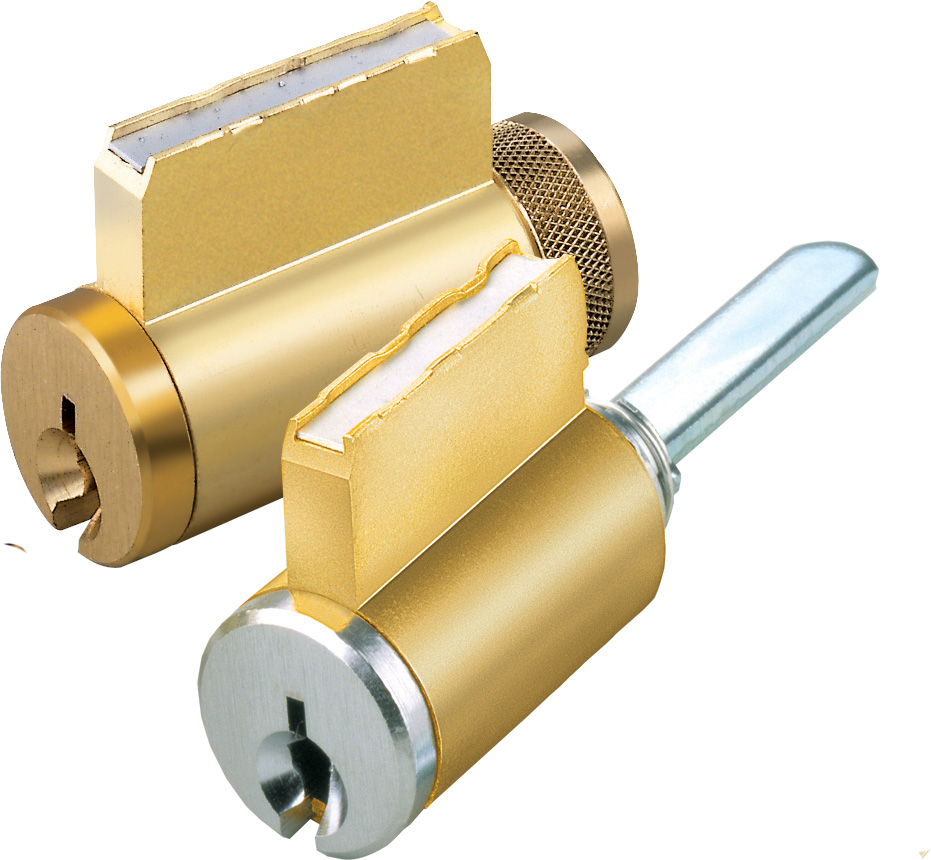
Cylinder: The Lock’s Heart
Job: The cylinder is at the heart of many locks. This is where locking and unlocking happen. The cylinder is a round chamber that holds pins or wafers. These line up with the key’s ridges and valleys. When you put the right key in and turn it, it lifts these pins or wafers to the right height. This lets the cylinder turn and unlock the lock.
Kinds: Cylinders can be different in design and how they work. The two most common kinds are pin tumbler and wafer tumbler cylinders. Pin tumbler cylinders have a series of pins of different lengths that are pushed up by springs. Wafer tumbler cylinders use flat, wafer-like parts. Both kinds rely on lining up their inside parts with the key’s pattern to unlock the lock.
Latch or Bolt: The Door Securer
Role: Latches or bolts are the last barrier against unwanted entry when the door is shut. These parts stick out from the lock into the door frame or strike plate. This secures the door in place. Without the right key or combination, the latch or bolt stays out, making the door stronger against break-ins.
Kinds: There are different kinds of latches and bolts, each offering different levels of security. Deadbolts, for example, give strong protection by sticking a solid metal bolt into the door frame when you turn the key. Latchbolts use a spring to keep the door in place. You often find these in inside doors and cabinets.

The internal component of the lock
Ever wonder what happens inside a lock when you turn the key? Let’s look at the parts that make a lock work. Springs, pins, and other parts all help to keep our stuff safe.
Springs: The Quiet Helpers
Job: Springs in a lock are like quiet heroes. They give tension and bounce to moving parts. They make sure parts go back to where they started after you turn or take out the key. This keeps the lock working right.
Where They Are: You can find springs in many places in the lock. They’re usually next to pins or inside the main cylinder. Where they are is important for smooth movement and proper working of other parts.
Pins or Wafers: Exact Guards
Job: Pins or wafers are barriers in the lock. They stop the cylinder from turning until you put in the right key. When you put in the key, its special pattern lifts these pins or wafers to the right height. This lets the cylinder turn and unlock.
Setup: These small parts come in different shapes and sizes, depending on the lock. In pin tumbler locks, round pins are stacked in pairs. In wafer tumbler locks, flat wafers are side by side. How they’re set up decides how complex the lock is.
Driver Pins: Key Parts in Locking
Purpose: Driver pins make sure the lock stays locked until you use the right key. They sit on top of the key pins and push down. This makes a barrier that stops the cylinder from turning without the right key.
How They Work with Key and Plug: When you put the right key into the lock, its special pattern lines up with the driver pins. It lifts them to the exact height needed to line up the shear line. This lets the plug turn freely, unlocking the lock and letting you in.
Plug: The Part That Turns
Role: The plug is the main part of the lock. It connects the key to the cylinder and makes the lock work. When you put in the right key and turn it, the plug turns. This unlocks the lock and lets you open the door.
How It Connects to Key and Cylinder: The plug connects directly to both the key and the cylinder. It’s a key link in the chain of parts inside the lock. Its design and how it lines up with the key’s pattern decide if the lock can open or stay locked.
Extra Parts of Some Locks
Let’s talk about these extra features. They make locks better and safer.
Electronic Parts
These parts add new features to old lock systems. They make locks safer and easier to use. Sensors in the lock can sense things like movement or how close something is. These sensors can make the lock open or close quickly. The lock’s circuits are like its brain. They take signals from the sensors and tell the lock what to do. All these parts work together to make the lock stronger against unwanted entry.
The power source is a key part. It gives power to these electronic parts. This power can come from batteries or wires. A steady power source makes sure the lock works all the time. Adding electronic parts makes locks smarter and quicker to react. They become better at keeping things safe.
Biometric Parts
These parts change the way locks check who is trying to open them. They are very accurate and reliable. A biometric scanner usually checks fingerprints or eyes to see who is trying to open the lock. This new way of checking is safer than old ways, like keys or passwords that can get lost or forgotten.
The scanner works with a database. This database is a safe place in the lock’s memory where it keeps allowed fingerprints or eye patterns. The database helps the lock check and approve people quickly when they try to open it. The lock compares the scanned fingerprint or eye with the ones it has saved. This way, the lock only lets in people who are allowed to enter. This makes the lock even safer.
